ERC-721 NFT Token
In this article, we will consider an ERC-721 NFT contract example. You will learn how to deploy and interact with it.
In case you are not familiar with a standard we advise you to read more about it on the OpenZeppelin website: ERC-721 article and ERC-20 API.
Here is the full contract code below:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721URIStorage.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.sol";
contract CovidVaccineToken is ERC721URIStorage {
uint256 private _tokensCount = 0;
address public minter = address(0);
modifier onlyMinter(){
require(
minter == msg.sender,
'Invalid Minter'
);
_;
}
constructor() ERC721("CovidVaccineToken", "CVT") {
minter = msg.sender;
}
function mint(address to) external onlyMinter {
uint256 tokenId = _tokensCount + 1;
_mint(to, tokenId);
_tokensCount = tokenId;
}
function burn(uint256 tokenId) external {
_burn(tokenId);
_tokensCount -= 1;
}
function safeTransferFrom(address from, address to, uint256 tokenId) public virtual override {
require(minter == msg.sender || to == minter, 'Invalid Transfer');
safeTransferFrom(from, to, tokenId, "");
}
function safeTransferFrom(address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, bytes memory _data) public virtual override {
require(minter == msg.sender || to == minter, 'Invalid Transfer');
require(_isApprovedOrOwner(_msgSender(), tokenId), "ERC721: transfer caller is not owner nor approved");
_safeTransfer(from, to, tokenId, _data);
}
}
You can find a GitHub repo and another version of this tutorial on Aurora Developer Portal.
This example is originally forked from the OpenZeppelin examples. However, the code has been changed to fit the use case of this tutorial. The use case is about how to deploy and manage the life cycle of a simple COVID-19 vaccine NFT token 💊 using Truffle on the Aurora Testnet.
Vaccine NFT Token Lifecycle
On the image below you can observe how a lifecycle of the Vaccine NFT token looks like:
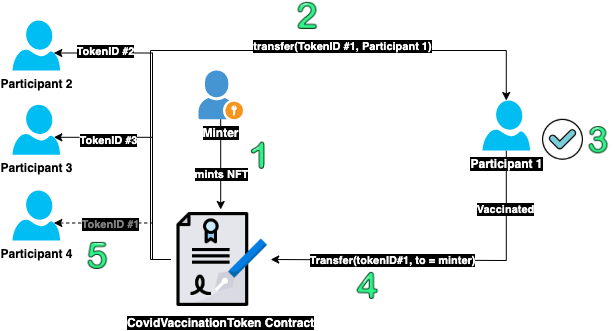
Let's describe it step by step:
-
The minter address (which is managed by the vaccination program manager) can distribute (mint) the vaccine tickets (NFT tokens 💊) to the people who are part of the vaccination program.
-
When participants receive the tokens 💊, they can get access to the vaccine by spending the NFT token.
-
This means either burning the NFT token or sending it back to the minter address.
-
If the participant chooses to send it back then the minter can redistribute that token to the other participant in the line.
-
Then the new participant will have access to the same vaccine token that has been used by the previous participant.
Create project
To create a project, clone the examples repository, go to erc-721-example folder, and install yarn dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/aurora-is-near/aurora-examples.git
cd aurora-examples/truffle/erc721-example/
yarn install
Configure project
Add your Mnemonic (from MetaMask or other Web3 wallet) to the environment variable:
export MNEMONIC='YOUR MNEMONIC HERE'
Now in truffle-config.js, you will need to change the from address as shown
below in the aurora network section:
...
aurora: {
provider: () => setupWallet('https://testnet.aurora.dev'),
network_id: 0x4e454153,
gas: 10000000,
from: 0x6A33382de9f73B846878a57500d055B981229ac4 // change this to your address here
},
The truffle-config.js configuration will pick up your MNEMONIC environment
variable and recover the address that will be used for sending and signing
transactions on the Aurora network.
Deploy contract
To use the commands below you will need Node.js and yarn to be installed. Please follow the instructions here to install Node.js.
Then, install yarn with npm install --global yarn or read more here.
To deploy the CovidVaccineToken contract, you can run the yarn command as
follows:
yarn deploy:aurora
....
_deploy_contracts.js
=====================
Deploying 'CovidVaccineToken'
-----------------------------
> transaction hash: 0x282012c791d65d0ce2fd1fd9fcc41179dba5bd06c3b02e31e53dbe9cc8af62c1
> Blocks: 7 Seconds: 5
> contract address: 0x3635D999d8CdA2fAf304b390fb26a9c2f364dFbd
> block number: 49151611
> block timestamp: 1622034185
> account: 0x6A33382de9f73B846878a57500d055B981229ac4
> balance: 0
> gas used: 2576274 (0x274f92)
> gas price: 20 gwei
> value sent: 0 ETH
> total cost: 0.05152548 ETH
....
Playing with the Truffle Console
Now you can test the flow as mentioned in the NFT Example section:
Mint tokens
The minter mints and transfers NFT tokens for the vaccine program participant.
In this example, the new participant address is
accounts[1] and the minter address is accounts[0].
Please make sure that you are using the same deployer address as a minter
address, otherwise the mint transaction will revert.
% truffle console --network aurora
truffle(aurora)> const cvt = await CovidVaccineToken.deployed()
truffle(aurora)> const minter = accounts[0]
truffle(aurora)> const participant = accounts[1]
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.minter() == minter
true
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.mint(participant, {from: minter})
You should notice that none of the participants are allowed to transfer their NFT tokens to anyone except back to the minter.
So let's try to use any participant address to validate this. To do that, change
the value of from to accounts[1], so that the sender will be the first
participant (e.g., the participant address
0x2531a4D108619a20ACeE88C4354a50e9aC48ecfe).
In the Truffle console:
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.safeTransferFrom(participant, accounts[2], 1, {from: participant})
Uncaught Error: execution reverted:
...
reason: 'Invalid Transfer',
hijackedStack: 'Error: execution reverted:\n'
This is exactly the same error message we have in our NFT contract in
safeTransferFrom:
function safeTransferFrom(
address from,
address to,
uint256 tokenId
)
public
virtual
override
{
require(
minter == msg.sender || to == minter,
'Invalid Transfer'
);
safeTransferFrom(from, to, tokenId, "");
}
Transfer tokens
Participants can transfer the token to the minter after receiving the vaccine.
As shown below, a participant can only send the NFT token if the receiver for
this token is the minter (accounts[0]).
truffle(aurora)> const tokenID = 1
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.ownerOf(tokenID) == participant
true
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.safeTransferFrom(participant, minter, tokenID, {from: participant})
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.ownerOf(tokenID) == minter
true
Burn tokens
This is an alternative scenario for the NFT token lifecycle. Instead of
transferring the token back to the minter, the participant can decide to burn the
NFT token by calling the burn function:
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.burn(1, {from: participant}) // 1 is the tokenID
Redistribute tokens
Finally, the minter can send the same token (if not burnt) to a new participant in the line:
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.safeTransferFrom(minter, accounts[2], 1, {from: minter})
truffle(aurora)> await cvt.ownerOf(1) == accounts[2]
true
Summary
In this simple tutorial, we deployed an NFT contract to the Aurora Testnet using Truffle and interacted with the contract's functions.